Hey there! Have you ever seen those photos where just one color makes the whole image stand out? Today, we’re going to unpack monochrome image definition, show you how it’s different from your usual black and white snapshots, and guide you through creating your own monochrome magic!
Let’s begin!
What is Monochrome Photography
 Monochrome photography comes from the Greek words "mono" (one) and "chromos" (color). It focuses on a single color and all its shades, from very light to very dark. This approach simplifies an image to one hue, creating a strong and unique look that can show more emotion and detail than color photos.
Monochrome photography comes from the Greek words "mono" (one) and "chromos" (color). It focuses on a single color and all its shades, from very light to very dark. This approach simplifies an image to one hue, creating a strong and unique look that can show more emotion and detail than color photos.
In the past, photographers used darkroom techniques like sepia toning for warm brown tones or cyanotype for cool blues to get these effects. Now, it’s much simpler to achieve these looks with digital tools. Thanks to digital tools, anyone can play around with these colors.
Transform Your Photos into Classic Monochrome
Try it in Luminar NeoMonochrome vs Black-and-White Photography
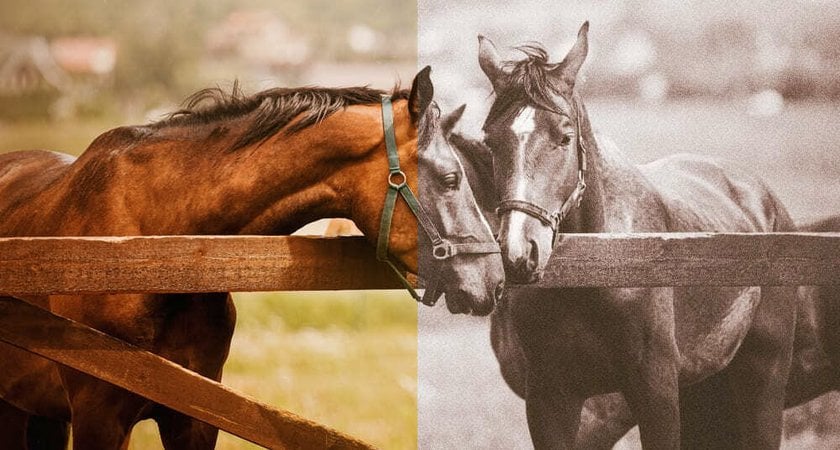
 Black-and-white photography sticks to black, white, and gray shades, a classic style that echoes the earliest days of film. Monochrome photography takes a broader approach. While it can include black and white, it can also focus on any single color. This means a photo might be all shades of blue, green, or any color you choose, opening up more creative possibilities beyond the traditional black and white. The use of one color can change the mood and focus of a photo, adding a unique atmosphere.
Black-and-white photography sticks to black, white, and gray shades, a classic style that echoes the earliest days of film. Monochrome photography takes a broader approach. While it can include black and white, it can also focus on any single color. This means a photo might be all shades of blue, green, or any color you choose, opening up more creative possibilities beyond the traditional black and white. The use of one color can change the mood and focus of a photo, adding a unique atmosphere.
In-Camera Monochrome Photography
 In-camera monochrome photography lets you take pictures that are all in one color right from your camera without needing any extra software. This works whether you're using a basic camera or a fancy DSLR.
In-camera monochrome photography lets you take pictures that are all in one color right from your camera without needing any extra software. This works whether you're using a basic camera or a fancy DSLR.
Adjusting the Camera Settings
First, set your camera to shoot in RAW format. This format captures all the details your camera sees. Unlike JPEG, which simplifies and compresses the image, RAW keeps everything so you can make more detailed edits later.
Many cameras have a special monochrome mode. This mode lets you see your scene in black and white or another single color through your camera's screen before you even take the picture. This helps you visualize how the final image will look. You can adjust settings to change how warm or cool the picture looks and even apply effects that mimic old-fashioned film styles. When you snap the photo, the camera saves one copy in black and white and keeps another copy in full color in RAW format.
Using Filters
Putting filters on your camera lens can also improve your monochrome photos, especially in bright light, or create specific effects like blurring moving water. Neutral density (ND) filters are helpful because they reduce the light coming into the camera without changing the colors. This helps prevent bright spots from being too overwhelming. Color filters are useful, too, if your camera is set to shoot in monochrome; they can make the darks darker and the lights lighter, which adds depth to your photos!
Considering Monochrome Cameras
There are also special cameras made just for taking monochrome pictures. However, these can be very expensive. Some people even modify their regular cameras to only take monochrome photos, but it's a big commitment because it's permanent and costly. For most people, using the monochrome settings on a regular camera and editing the RAW files later is enough to get creative and make great monochrome photos!
Exclusive Tools of Endless Possibilities in One AI Editor
EXPLORE NOW!How to Turn Color Photos into Monochrome

To convert a color photo into a monochrome image, you can use popular photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, or Luminar Neo. Here are steps to help you through the process in Luminar Neo!
- Open Your Photo: Add your photos to the Catalog by clicking “Add photo” or just drop them in the software from the folder.
- Convert to Grayscale: The first major step is to use the grayscale converter to transform your image. Go to the “Edit” page and find the “Black & White” tool in the Essentials tab. This tool removes all colors and leaves you with blacks, whites, and grays.
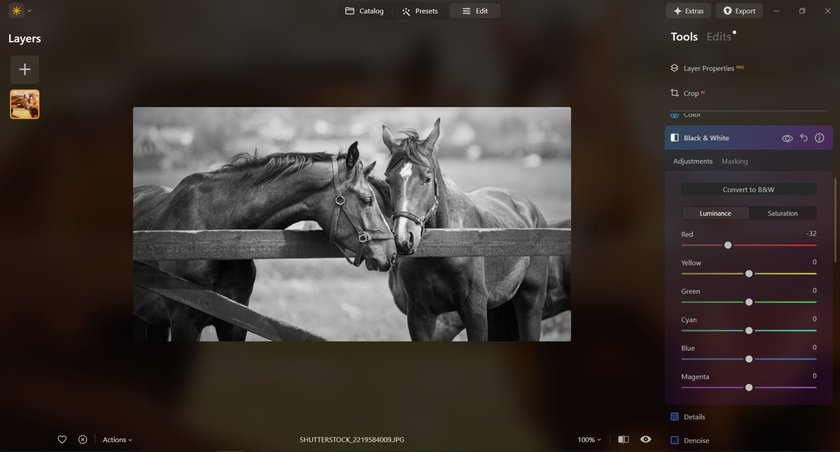
- Choose a Color Tool (Optional): If you want a tinted monochrome image (like sepia or cyan), you can use the image color changer to add a color layer or apply a color filter. This step is optional and depends on whether you prefer a traditional black-and-white image or one with a slight color tint. Adjust the color's intensity to achieve the effect you want.
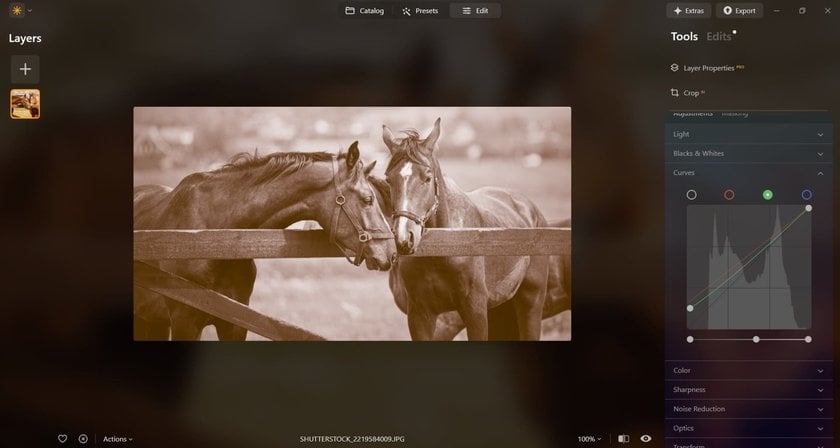
- Adjust Brightness and Contrast: This helps to highlight details, deepen shadows, and enhance the overall depth of the image. Further, tweak your image using adjustment layers or filters. Adjust levels or curves to refine the balance of light and dark areas. Use the Develop tool for this!
- Apply Adjustments and Filters: Further, tweak your image using adjustment layers or filters. Adjust levels or curves to refine the balance of light and dark areas. Experiment with presets specifically designed for monochrome or black-and-white looks to quickly explore different styles.
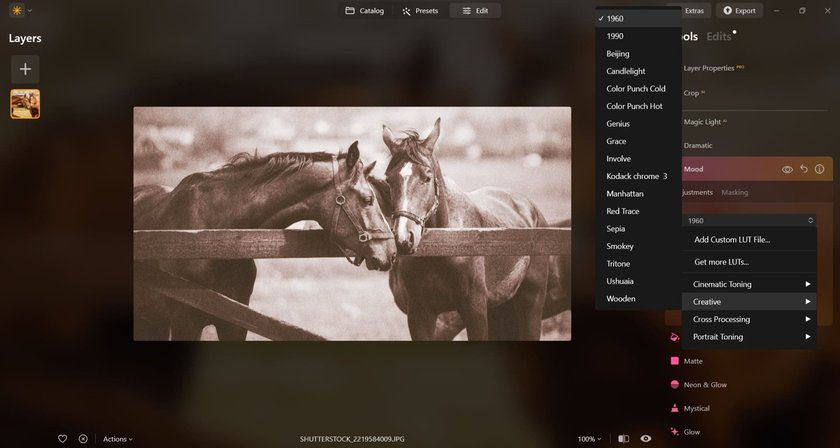
- Final Touches: Make any final adjustments to ensure the image looks just the way you want it. This might include sharpening the image, adjusting the exposure, or adding a vignette for artistic effect.
- Save Your Image: Once you’re satisfied with your monochrome image, save it in your preferred format. Make sure to keep an original copy in case you want to revert or make different edits later!
If You Want Just Black and White
 If you're aiming for that, Luminar Neo offers a quick solution with its feature to make the image black-and-white. This tool converts color images to black-and-white in just a few clicks, removing the need for manual desaturation or color adjustments. It is ideal for those seeking a classic black-and-white look without the complexities of manual tweaking!
If you're aiming for that, Luminar Neo offers a quick solution with its feature to make the image black-and-white. This tool converts color images to black-and-white in just a few clicks, removing the need for manual desaturation or color adjustments. It is ideal for those seeking a classic black-and-white look without the complexities of manual tweaking!
Redefine Your Photos with Black and White Filter
Try it NowTips for Stunning Monochrome Photography

- Scout the Right Scenes: Focus on locations with strong light contrasts and dynamic lighting, like during early morning or late evening. Subjects like landscapes, city views, and people often work well in monochrome.
- Try Converting Existing Photos: Practice turning your color photos into black-and-white to refine your editing skills and see what works.
- Emphasize Contrast: In monochrome, contrast brings depth and focus. Don't be shy about amplifying contrast during editing to enhance this effect. Read more about black-and-white contrast in our previous post!
- Focus on Composition: Without color to catch the eye, you really need to nail where things sit in your shot. Make sure your main subject stands out by how you arrange everything else around it.
- Experiment with Long Exposures: Long exposures are great for making moving water look smooth and surreal. This technique can turn an ordinary river or waterfall into a stunning black-and-white photo.
- Pay Attention to Textures and Patterns: In black and white, textures and patterns jump out way more. They can really grab attention and give your photo some punch.
- Use a Full Range of Tones: Using different shades of gray can give your photo more depth and make it look more sophisticated.
- Convey Emotion with Light and Shadow: Use the play of light and shadow to set the mood of your photo; it can become more dramatic and emotional.
- Leverage Shadows: Shadows aren’t just dark areas; they can add mystery and layers to your picture. Let them play a part in telling your photo's story.
Conclusion
So, this post covered the monochrome photography definition, explained how it's different from simple black-and-white, and showed you how to make these images yourself.
Enjoy your monochrome images!





